central america
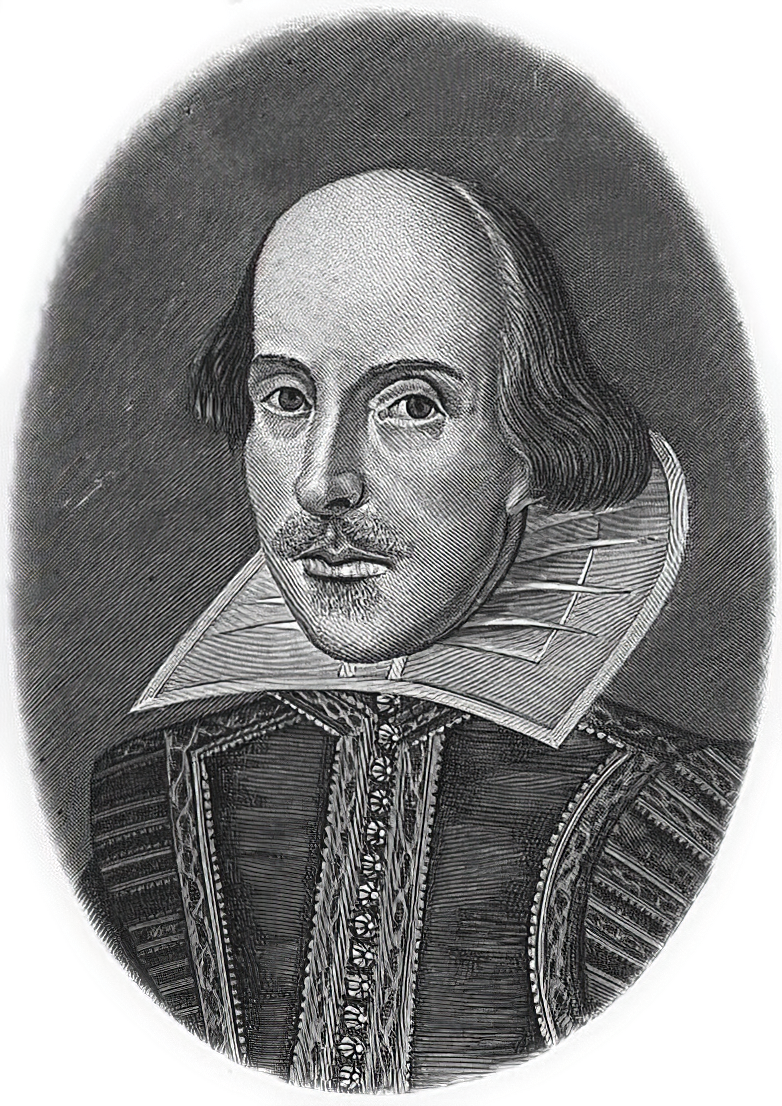

William Shakespeare was a British poet and playwright and writer.
William's father, John Shakespeare, was a merchant and official in Stratford. There are reports that he was a sailor for a time before joining a theater company in London. Beginning in the 1590s, Shakespeare began writing plays, and in 1593 he published a poem, Venus and Adonis, which became popular. He dedicated it to the Duke of Southampton, who was a philanthropist and patron of talent, and soon his business was booming.
From 1592 to 1600 Shakespeare wrote his dramas and romantic comedies "Richard III", "The Taming of the Shrew", "Romeo and Juliet", "A Midsummer Night's Dream" and "The Merchant of Venice", as well as the comedies "Much Ado About Nothing", "Twelfth Night" and the tragedy "Julius Caesar". The playwright's business was so successful that he even bought a large house in Stratford. In 1599, Shakespeare became one of the owners, playwright and actor of the new theater "Globe". In 1603 King James took Shakespeare's troupe under his direct patronage. In the mature period, the great playwright turned to tragedies, there were "Hamlet", "Othello", "King Lear", "Macbeth" and others.
Although in the 19th century researchers had some doubts about the authorship of many of these works, William Shakespeare is considered the greatest English playwright, one of the best playwrights in the world. His plays have been translated into all major languages and to this day form the basis of the world theatrical repertoire, most of them have been screened many times. According to the Guinness Book of Records, Shakespeare remains the world's best-selling playwright, and his plays and poems have sold more than 4 billion copies in the nearly 400 years since his death.


Nathaniel Niles is an American lawyer and politician, a member of the House of Representatives from Vermont.
Niles attended Harvard College and the College of New Jersey, eventually becoming a preacher but also active in politics. Niles sat in the lower house of the Vermont legislature for eight terms. From 1784 to 1787 he was a member of the state supreme court.
In addition to his sermons, he published numerous theological articles. When the American Revolution broke out in 1775, Niles enthusiastically supported the war against England. He even wrote his only work of poetry, an ode entitled "American Hero," to commemorate the Battle of Bunker Hill, which was set to music and became quite popular among New England soldiers and militia.
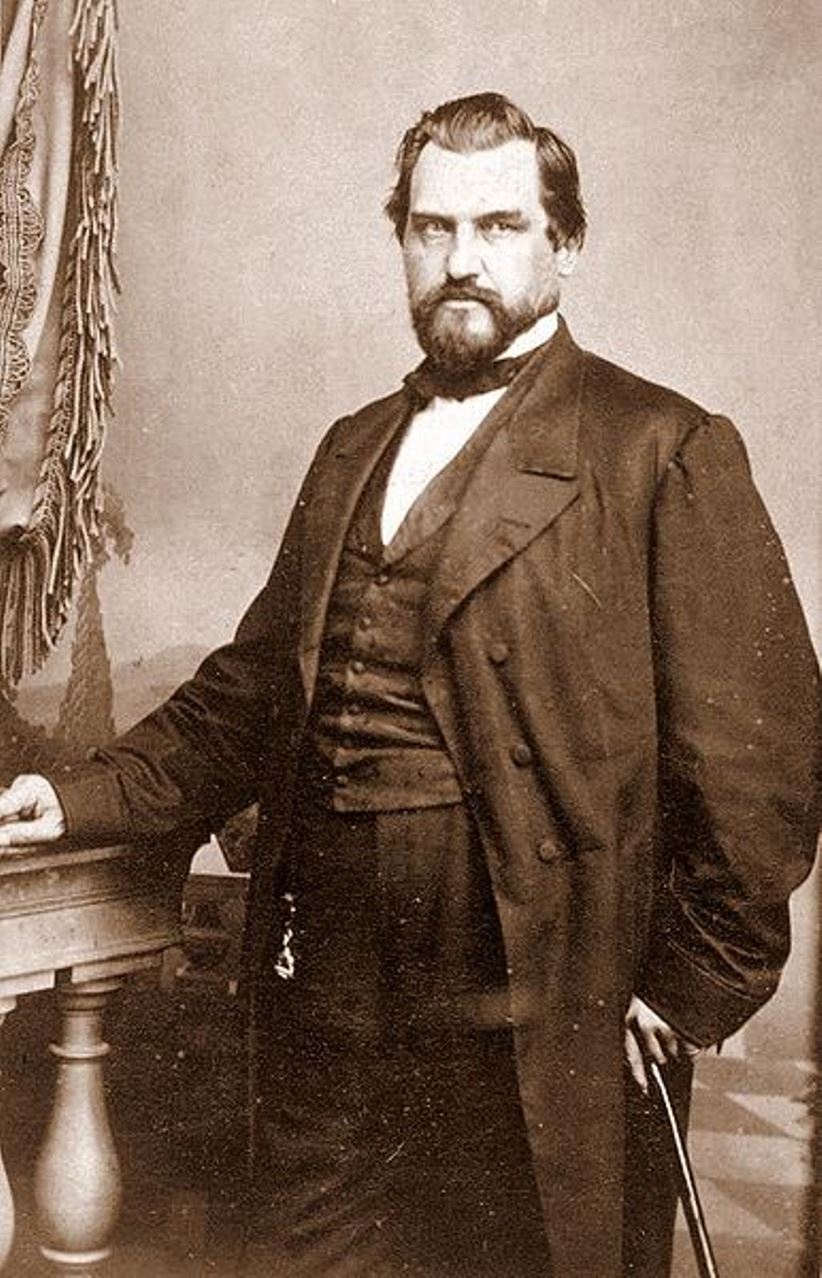


Amasa Leland Stanford was an American politician, industrialist and entrepreneur, and founder of Stanford University.
Born into a wealthy family, Stanford earned a law degree and practiced law in Wisconsin, and soon built a lucrative business selling mining equipment in northern California. And of course he became involved in politics, first as a justice of the peace and in 1861 was elected governor of California, but he didn't move away from business either.
As a member of the "Big Four" of the Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR), he was involved in planning the eastern section of the transcontinental railroad and helped secure major public investments and land grants for the railroad project. In 1863, Stanford became president of the Central Pacific Railroad and held that position for the rest of his life. He was also president of the Southern Pacific Railroad (which was acquired by the CPRR) and owned many of the construction companies that built the railroad. At the same time, he served in the U.S. Senate from 1885.
In 1891, he and his wife Jane Stanford founded Leland Stanford Junior University in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford, Jr. who died in his teens of typhoid fever during a trip to Italy.
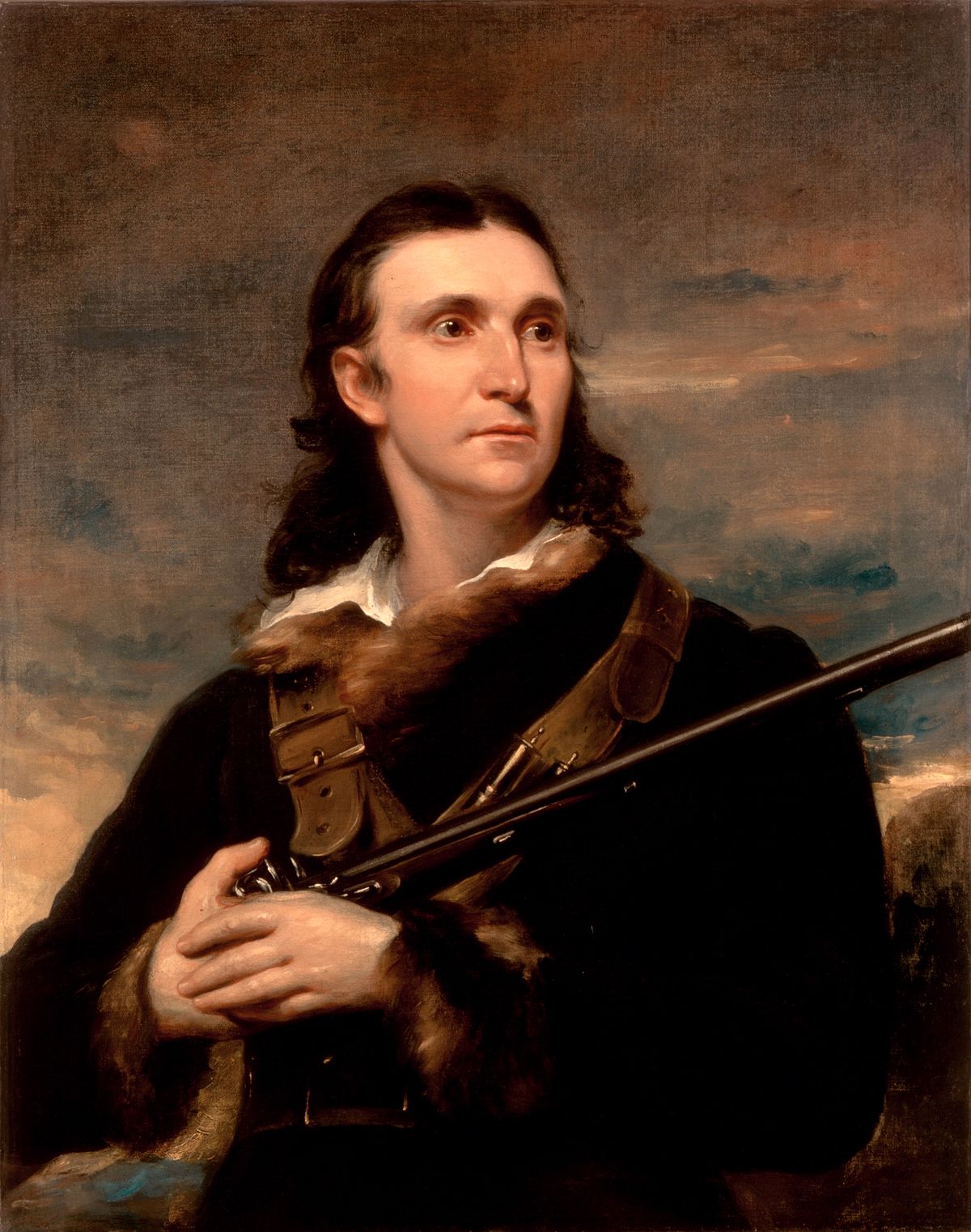


John James Audubon was a French-American ornithologist and painter, renowned for his groundbreaking illustrations of American birds. Born in 1785 in Les Cayes, Saint-Domingue (now Haiti), Audubon is remembered for his keen observation skills and innovative artistic techniques.
Audubon's most famous work, "The Birds of America," transformed the field of ornithology by presenting birds in lifelike poses and detailed backgrounds. Published between 1827 and 1838, it contained 435 hand-colored engravings, showcasing over 489 bird species. His unique approach to illustrating birds in their natural habitats was a departure from traditional methods, which often portrayed birds in rigid poses.
Audubon used a wire armature to position freshly-killed specimens, allowing him to depict birds with a sense of movement and vitality. This innovative technique was truly revolutionary and set him apart from his contemporaries. Additionally, Audubon's artistic skill and attention to detail made his illustrations highly sought after, with surviving copies of "The Birds of America" considered valuable collectibles today.
For art collectors and enthusiasts, Audubon's work continues to be a source of inspiration and admiration. His legacy endures through his contributions to ornithology and the art world, with museums and galleries showcasing his work. If you're interested in learning more about John James Audubon and his famous illustrations, consider subscribing to our newsletter for updates on new product sales and auction events related to his work.



Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.